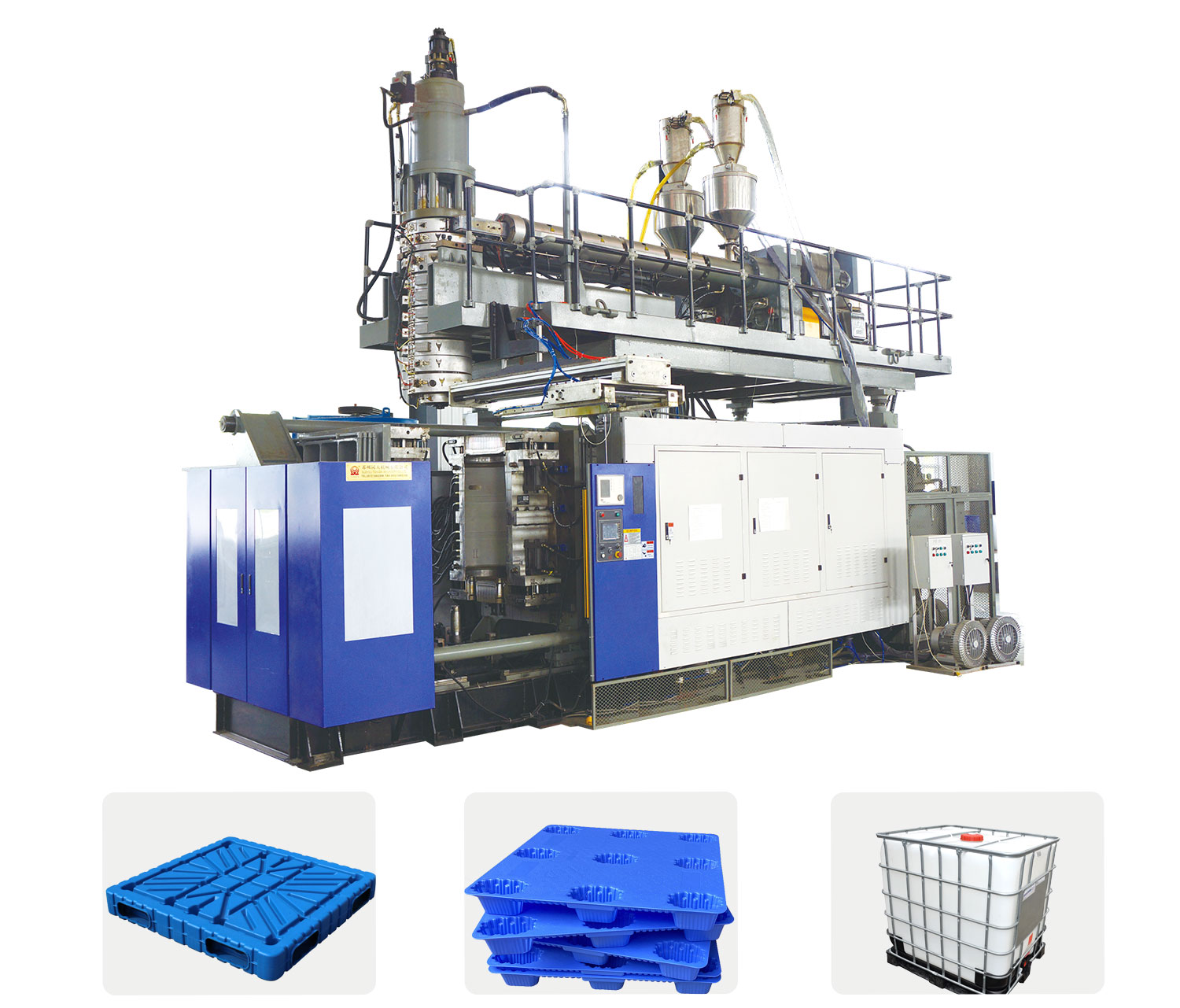
What do you know about common plastic processing methods?
Material processing, also known as plastic molding processing, is a general term for various processes for converting synthetic resins or plastics into plastic products, and is a large production department in the plastics industry. Using ethylene as the main raw material, propylene, 1-butene and hexene are copolymers. Under the action of the catalyst, the obtained polymer is flashed, separated, dried, granulated, etc. by slurry polymerization or gas phase polymerization. In the process, a finished product having uniform particles is obtained. These include, for example, sheet extrusion, film extrusion, tube or profile extrusion, blow molding, injection molding, and rotational molding.
Processing methods for plastic products:
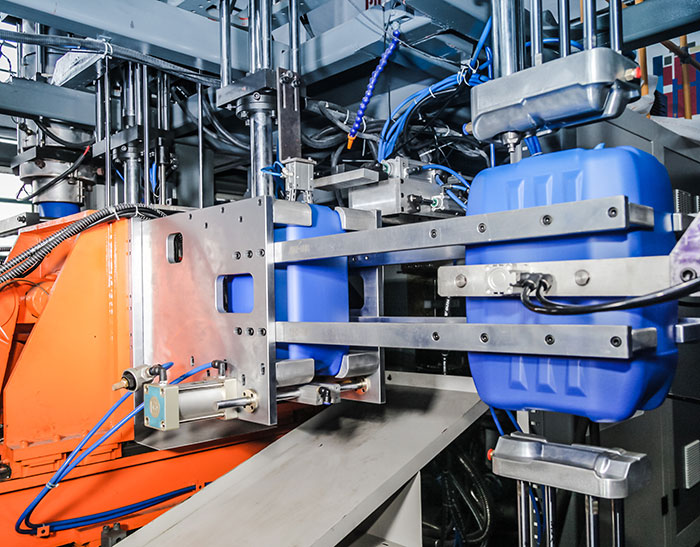

Extrusion:
Grades for extrusion production typically have a melt index of less than 1 and a medium to wide MWD. A low MI gives a suitable melt strength during processing. The wider MWD grade is more suitable for extrusion because of their higher production speed, lower die pressure and reduced melt fracture tendency.
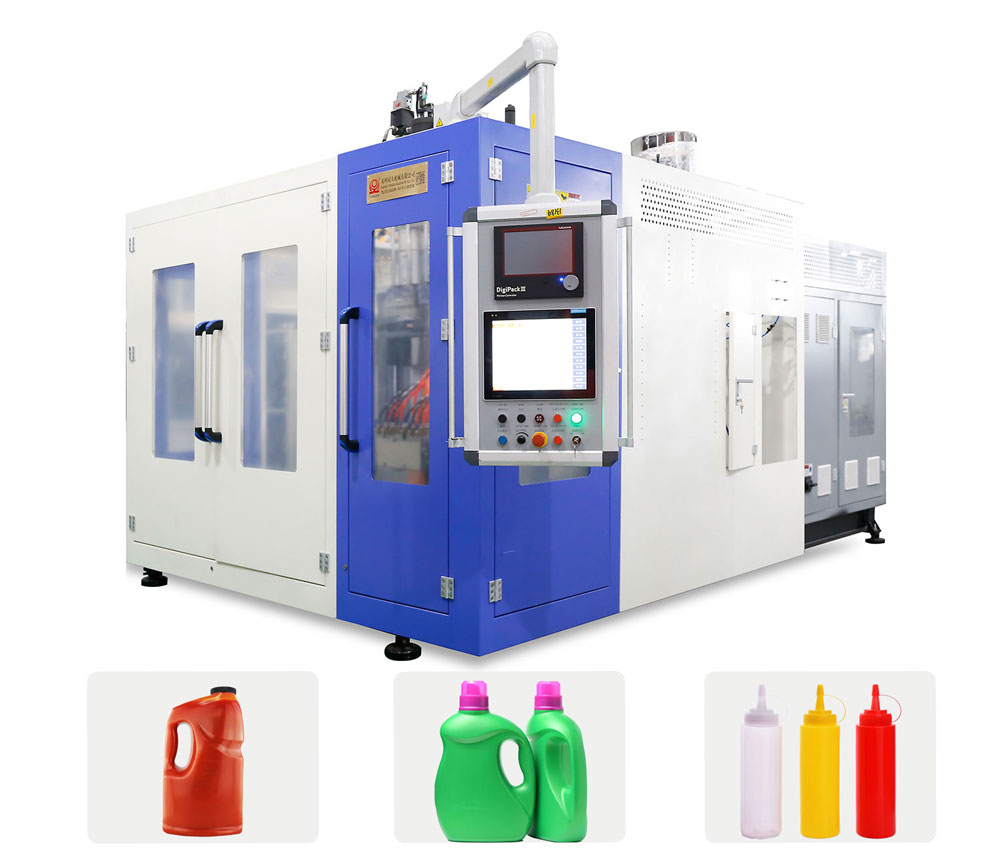
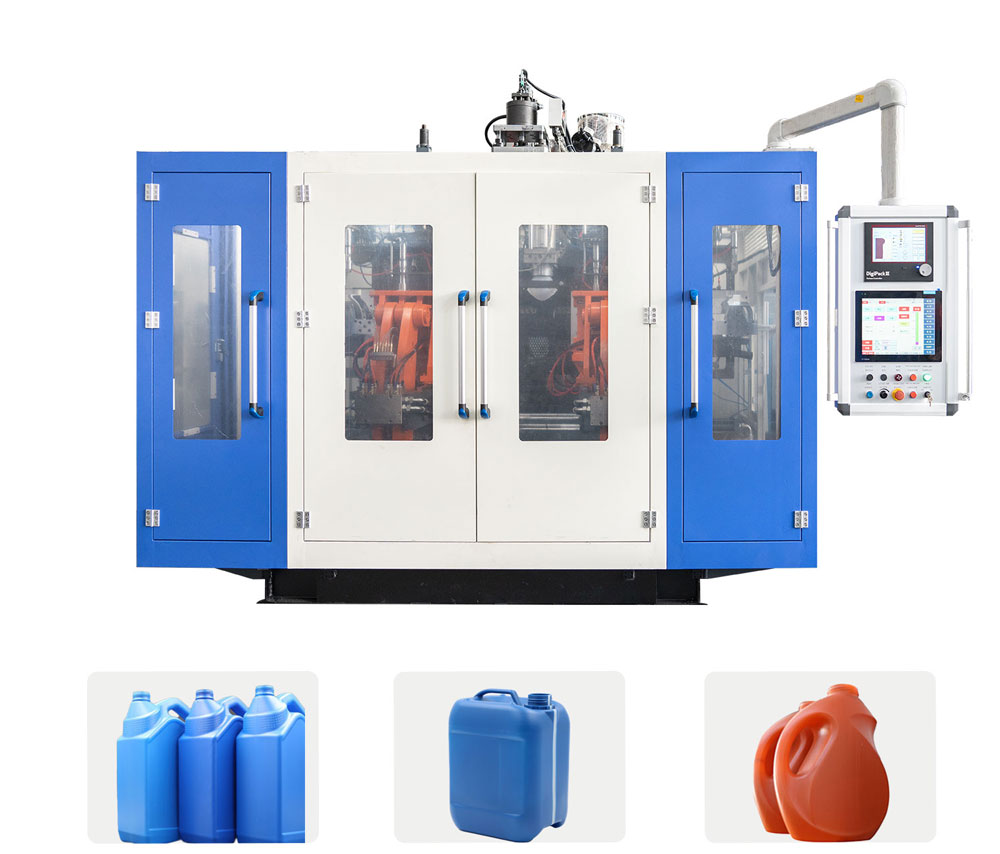
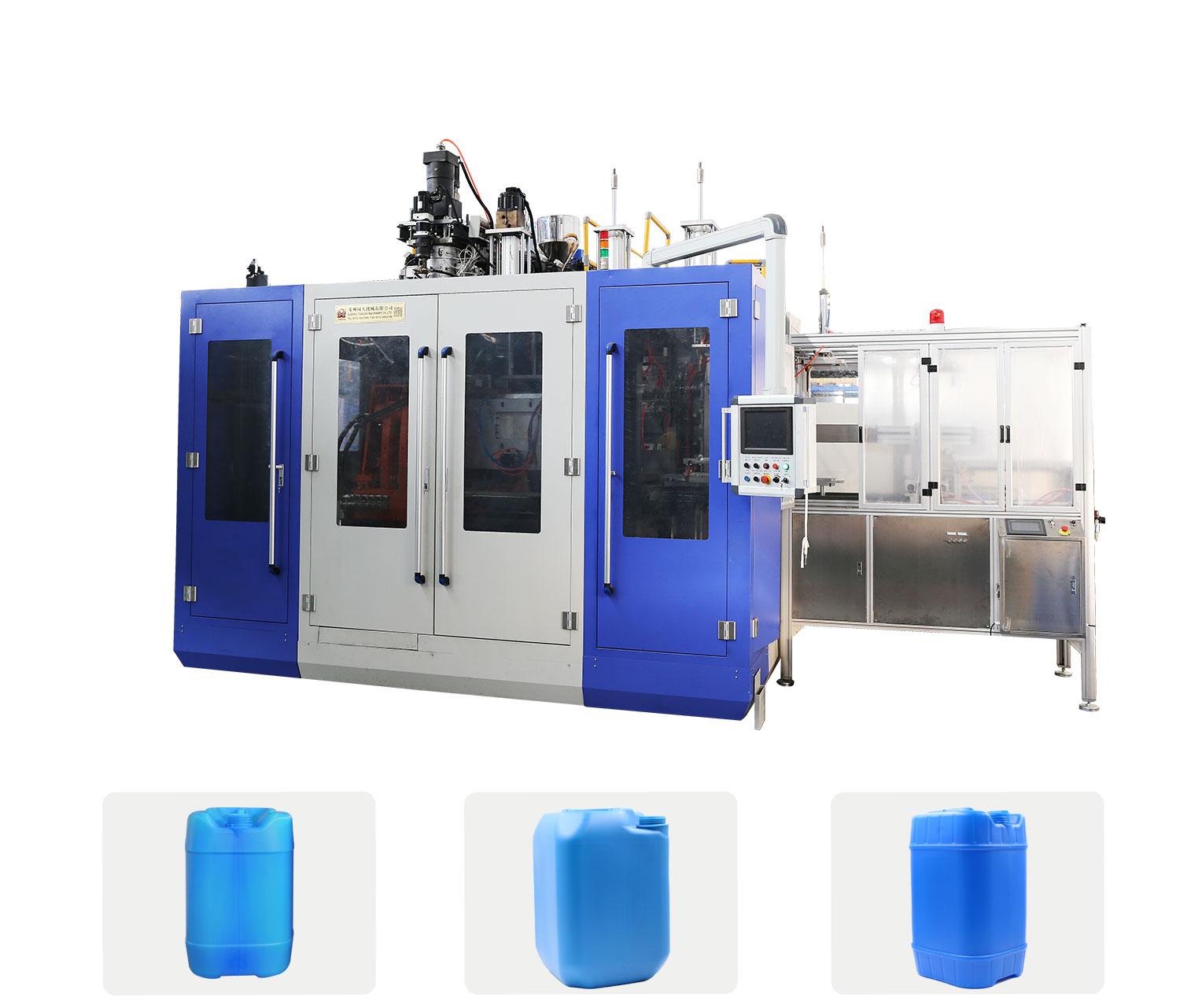
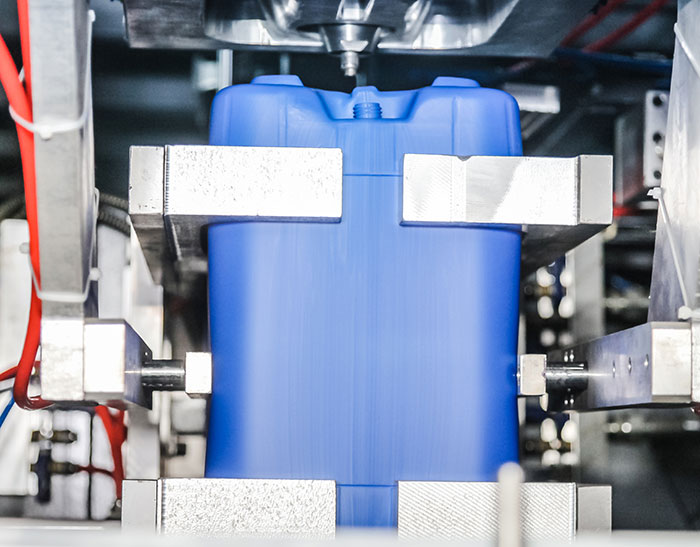
Blow molding: HDPE 1/3 or more sold in the United States is used for blow molding purposes. These range from bottles containing bleach, motor oil, detergents, milk and distilled water to large refrigerators, car fuel tanks and canisters. Blow molding grade characteristics such as melt strength, ES-CR and toughness are similar to those used for sheet and thermoforming applications, so blow molding machines can be used for similar grades. Blow molding machine
Injection molding: There are countless applications for HDPE, ranging from reusable thin-walled beverage cups to 5-gsl cans, which consume 1/5 of domestically produced HDPE. Injection molding grades generally have a melt index of 5 to 10, and have a higher flowability grade with a lower toughness grade and processability. Uses include daily necessities and food thin wall packaging; tough, durable food and paint cans; high environmental stress cracking applications such as small engine fuel tanks and 90-gal trash cans. Rotational molding: Materials using this processing are generally comminuted into a powder which is melted and flows in a thermal cycle. Rotational molding uses two types of PE: general purpose and crosslinkable classes. General purpose MDPE/HDPE typically has a density ranging from 0.935 to 0.945 g/cc and has a narrow MWD for high impact and minimal warpage, with a melt index typically ranging from 3-8. Higher MI grades are generally not applicable because they do not have the desired impact and environmental stress crack resistance of rotomoulded articles.
High performance rotational molding applications utilize the unique properties of their chemically crosslinkable grades. These grades are fluid in the first stage of the molding cycle and then cross-linked to form their excellent resistance to environmental stress cracking and toughness. Abrasion resistance and weather resistance. The cross-linkable PE is uniquely suited for use in large containers ranging from 500-gal to various chemical storage tanks to 20,000-gal agricultural storage tanks.
Blow molding: HDPE 1/3 or more sold in the United States is used for blow molding purposes. These range from bottles containing bleach, motor oil, detergents, milk and distilled water to large refrigerators, car fuel tanks and canisters. Blow molding grade characteristics such as melt strength, ES-CR and toughness are similar to those used for sheet and thermoforming applications, so blow molding machines can be used for similar grades. Blow molding machine
Injection molding: There are countless applications for HDPE, ranging from reusable thin-walled beverage cups to 5-gsl cans, which consume 1/5 of domestically produced HDPE. Injection molding grades generally have a melt index of 5 to 10, and have a higher flowability grade with a lower toughness grade and processability. Uses include daily necessities and food thin wall packaging; tough, durable food and paint cans; high environmental stress cracking applications such as small engine fuel tanks and 90-gal trash cans. Rotational molding: Materials using this processing are generally comminuted into a powder which is melted and flows in a thermal cycle. Rotational molding uses two types of PE: general purpose and crosslinkable classes. General purpose MDPE/HDPE typically has a density ranging from 0.935 to 0.945 g/cc and has a narrow MWD for high impact and minimal warpage, with a melt index typically ranging from 3-8. Higher MI grades are generally not applicable because they do not have the desired impact and environmental stress crack resistance of rotomoulded articles.
High performance rotational molding applications utilize the unique properties of their chemically crosslinkable grades. These grades are fluid in the first stage of the molding cycle and then cross-linked to form their excellent resistance to environmental stress cracking and toughness. Abrasion resistance and weather resistance. The cross-linkable PE is uniquely suited for use in large containers ranging from 500-gal to various chemical storage tanks to 20,000-gal agricultural storage tanks.











